
Data source list | Genomic Variants | ClinVar | COSMIC | Orthologue Alignments | Mastermind


|
Table of Contents
: Data Sources
: Data source list | Genomic Variants | ClinVar | COSMIC | Orthologue Alignments | Mastermind |

|
Alamut® Visual provides a convenient access to several databases of known variants listed below.
You can export all these variants (as well as ClinVar and Cosmic variants) in tabular format from a selected region defined in the transcript track. Click here for more information.
Classified genomic variants from ClinVar are also available. Click here for more information.
![]() Database versions of each source is available here.
Database versions of each source is available here.
![]() gnomAD is enabled by default for all users, whereas HGVD and GoNL are enabled by default only for Japanese and Dutch users respectively, based on their computer's region settings.
gnomAD is enabled by default for all users, whereas HGVD and GoNL are enabled by default only for Japanese and Dutch users respectively, based on their computer's region settings.
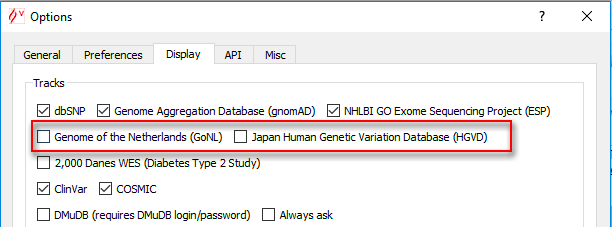
To enable or disable manually these databases, click on Tools > Options > Display and select or unselected data sources in the "Tracks" part.
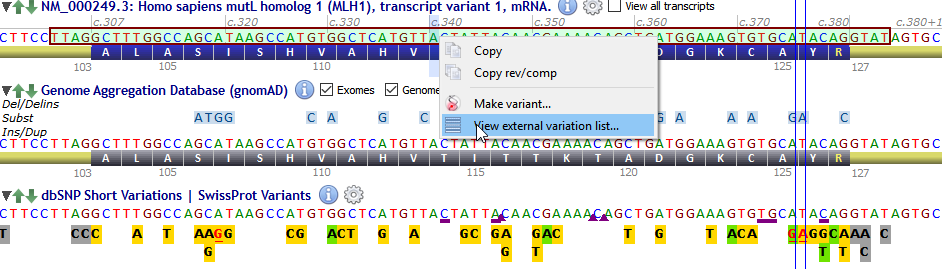
![]() To visualize and export known external variants, select a region of interest in the transcript track, right click on the selected region and, select 'View external variation list...' as shown below:
To visualize and export known external variants, select a region of interest in the transcript track, right click on the selected region and, select 'View external variation list...' as shown below:
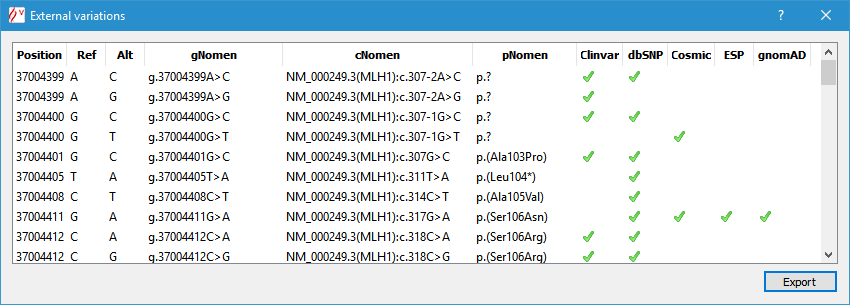
Then a new window appears and lists all external variants from the selected region. From this window, you can export this list into a text file (.csv) by clicking on the export button.
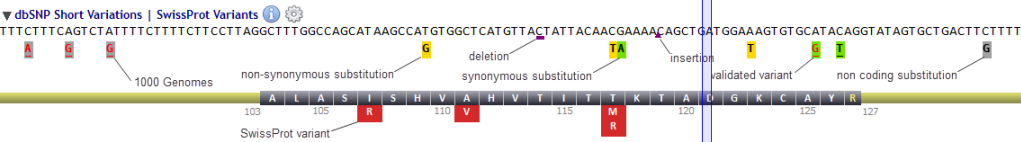
The following convention is used:
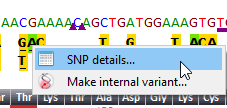
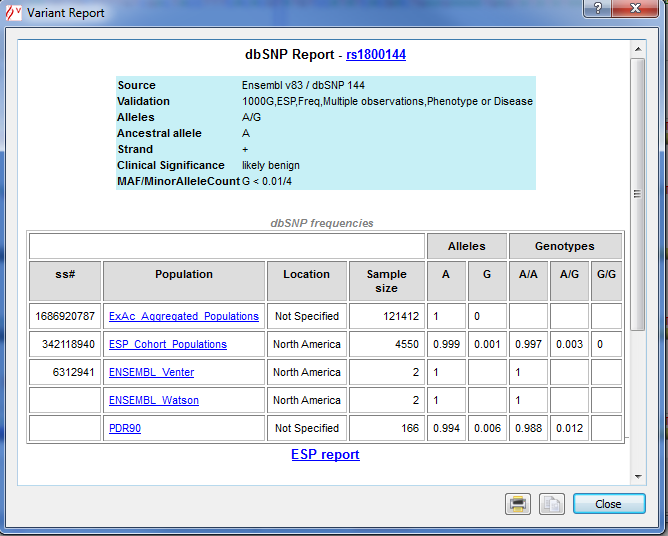
![]() Right click on a dbSNP variant opens a detailed report including, when available, Clinical significance, Evidence status, global minor allele frequency
(MAF), Ancestral allele and, Allelic and Genotype Frequencies in populations.
Right click on a dbSNP variant opens a detailed report including, when available, Clinical significance, Evidence status, global minor allele frequency
(MAF), Ancestral allele and, Allelic and Genotype Frequencies in populations.
 |
 |
 |
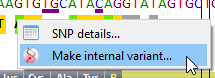
![]() Right click on a dbSNP variant enables to create directly a corresponding internal variant.
Right click on a dbSNP variant enables to create directly a corresponding internal variant.
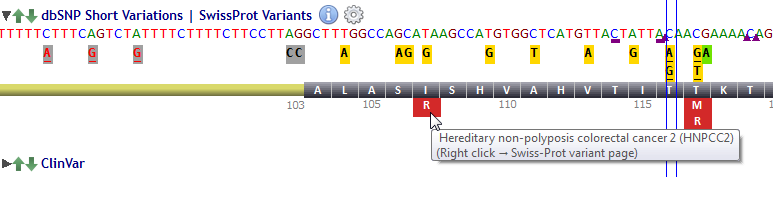
![]() Right click on a Swiss-Prot variant opens directly the Swiss-Prot variant page.
Right click on a Swiss-Prot variant opens directly the Swiss-Prot variant page.
The ESP goal is to discover novel genes and mechanisms contributing to heart, lung and blood disorders.
![]() Only variants having passed all ESP filtering criteria are shown in Alamut® Visual.
For more details see: ESP Filter Status.
Only variants having passed all ESP filtering criteria are shown in Alamut® Visual.
For more details see: ESP Filter Status.
The following convention is used:
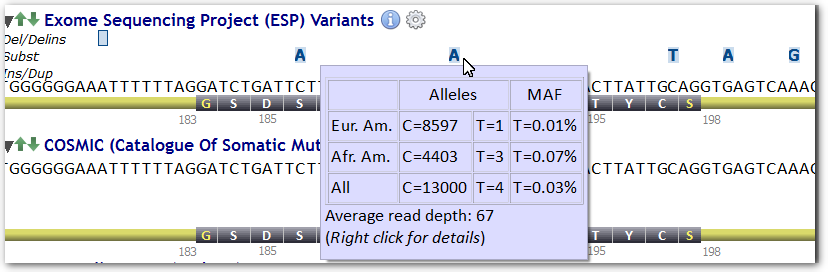
Populations size and minor allele frequencies (MAF) are displayed whenever the mouse cursor passes over.
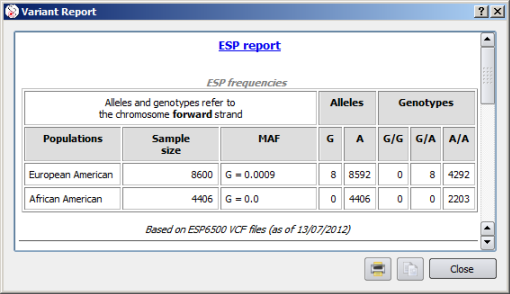
![]() Right click on an ESP variant opens a detailed report including allelic and genotype frequencies in populations.
Right click on an ESP variant opens a detailed report including allelic and genotype frequencies in populations.
 |
 |
 |
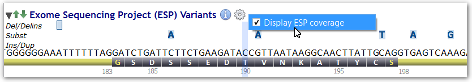
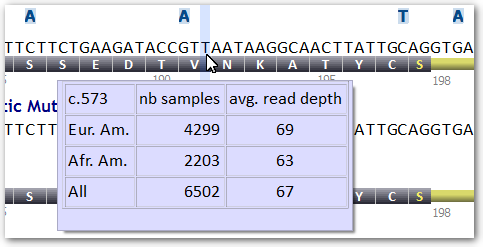
Starting with Alamut® Visual 2.3 (released in April 2013), the ESP track holds a new feature displaying sample size and average read depth by position and by population when these data are available.
 |
 |
 |
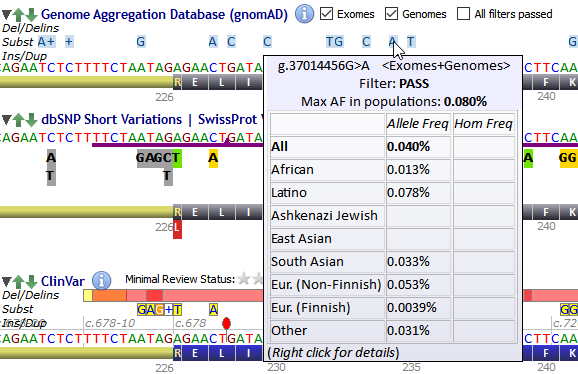
gnomAD variants are displayed as shown below. If multiple single nucleotide variants are reported at the same position a blue background is displayed along with a "+" sign.
Both gnomAD Exomes and gnomAD Genomes are included. Checkboxes near the track title allow to include or exclude exome or genome variants.
The 'All filters passed' option is unchecked by default. When checked only variants with all filters passed for at least one of the alleles at the site are displayed.
Hovering the mouse over a gnomAD variant pops-up a tooltip showing allele frequencies and homozygote genotype frequencies per population. (Hovering over a multiple-SNVs location pops-up an intermediate menu with entries for each individual variant). Data of variants found in both exomes and genomes are merged as in the gnomAD website. Estimated read depth is also displayed, except in the case of merged variants.
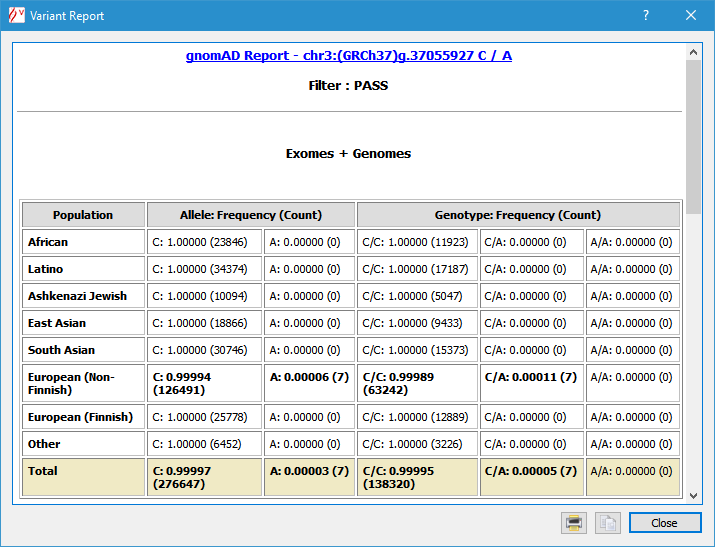
Right-clicking a variant pops-up a more detailed panel, including genotype counts and frequencies:
The Human Genetic Variation Database (HGVD) aims to provide a central resource to archive and display Japanese genetic variation and association between the variation and transcription level of genes.
![]() Both filtered and passing calls are shown in Alamut® Visual. For more details see: HGVD Data Generation (in preparation).
Both filtered and passing calls are shown in Alamut® Visual. For more details see: HGVD Data Generation (in preparation).
By default, in Alamut® Visual, variants without filter status information are passing calls.
The following convention is used:
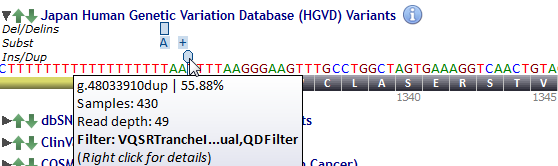
Allele frequency, number of samples covered, estimated read depth, filter status are displayed whenever the mouse cursor passes over.
![]() Right click on an HGVD variant opens directly the Human Genetic Variation Browser for the selected variant.
Right click on an HGVD variant opens directly the Human Genetic Variation Browser for the selected variant.
The GoNL Project aims to provide a single-population whole-genome sequencing with detailed characterization of genetic variation.
![]() Both filtered and passing calls are shown in Alamut® Visual. For more details see: GoNL Data Generation.
Both filtered and passing calls are shown in Alamut® Visual. For more details see: GoNL Data Generation.
By default, in Alamut® Visual, variants without filter status information are passing calls.
The following convention is used:
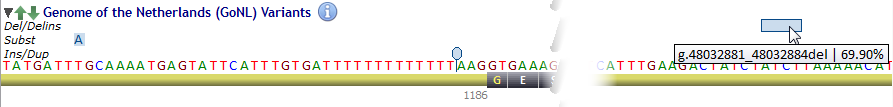
Allele frequency is displayed whenever the mouse cursor passes over.
![]() Right click on an GoNL variant is not implemented. Currently, it is not possible to open directly the GoNL Browser for the selected variant.
Right click on an GoNL variant is not implemented. Currently, it is not possible to open directly the GoNL Browser for the selected variant.
Database of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (dbSNP). Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information, National Library of Medicine. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/SNP/.
Exome Variant Server, NHLBI Exome Sequencing Project (ESP), Seattle, WA (URL: http://evs.gs.washington.edu/EVS/).
Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD), The Broad Institute (URL: http://gnomad.broadinstitute.org).
The Japan Human Genetic Variation Database (HGVD), Japanese genetic variation consortium (URL: http://www.genome.med.kyoto-u.ac.jp/SnpDB).
The Genome of the Netherlands Consortium. Whole-genome sequence variation, population structure and demographic history of the Dutch population. Nature Genetics (2014) doi:10.1038/ng.3021.(URL: http://www.nlgenome.nl/).
Whole-exome sequencing of 2,000 Danish individuals and the role of rare coding variants in type 2 diabetes. Am J Hum Genet. 2013 Dec 5;93(6):1072-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.11.005. Epub 2013 Nov 27.
© 2020 Interactive Biosoftware - Last modified: 3 June 2019