
Entering Variants | Variants annotations | Importing variants | Exporting & reporting variants


|
Table of Contents
: Managing variants
: Entering Variants | Variants annotations | Importing variants | Exporting & reporting variants |

|
Alamut® Visual allows you to annotate and store variants handled through the software.
Alamut® Visual allows you to define several variant folders and to easily switch from one to another. Alamut® Visual enables also to list and navigate easily through all internal variants for the current gene (menu 'Variants' > 'View internal variant List') or for any gene (menu 'Variants' > 'View all internal variants').
Variant annotations can be exported and reported to customizable external files and reports
(see Exporting & Reporting) but also be imported from external files (see
Importing Variants).
The basic variant database functionality implementation relies on files stored either on each user's computer, or on a shared file system.
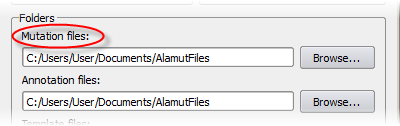
Variants are stored in local variant files, inside a folder that can be specified
in the Options dialog box (menu 'Tools' > 'Options' > 'Preferences' tab). By default, this folder is
'AlamutFiles' (inside 'My Documents' on Windows XP or Windows 7, inside 'Documents' on Windows Vista,
and inside the user's home folder on Mac and Linux):
Alamut® Visual creates individual variant files per gene, named after the gene's official symbol
and with extension 'mut' (e.g. MLH1.mut for MLH1 variants and DMD.mut for
DMD variants).
![]() It is also possible to define a set of different folders for variant files (menu 'Folders' > 'Variants').
It is also possible to define a set of different folders for variant files (menu 'Folders' > 'Variants').
These folders can be used for different use cases or projects and the menu enables to easily switch from one folder to another:
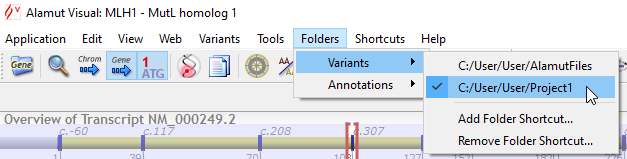
When switching to another folder, the only visible variants are those that are stored in a file within the selected folder, if any.
The first listed folder shortcut in the menu is always the one that has been defined
in the Options dialog box (menu 'Tools' > 'Options' > 'Preferences' tab, see above).
Extra folder shortcuts can be added or removed from the menu.
![]() As for any important computer data, please backup variant files regularly.
As for any important computer data, please backup variant files regularly.
![]() When variants are stored in a shared file system, caution must be taken so that 2 people don't edit concurrently variants of the same gene.
When variants are stored in a shared file system, caution must be taken so that 2 people don't edit concurrently variants of the same gene.
Variant files use a simple XML representation format, suitable for processing by other applications. Furthermore, variants can be exported to tab-delimited flat text files that can be easily imported into spreadsheet applications.
Create variants either from the 'Variants' menu, or from a nucleotide selection in the transcript track and its associated context menu (by right-clicking inside the selection).
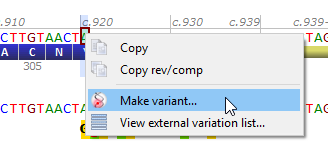
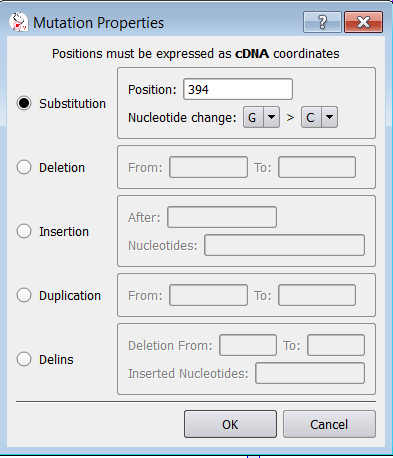
Once you have specified variant basic properties (position and type of change), the annotation window pops up:
 |
 |
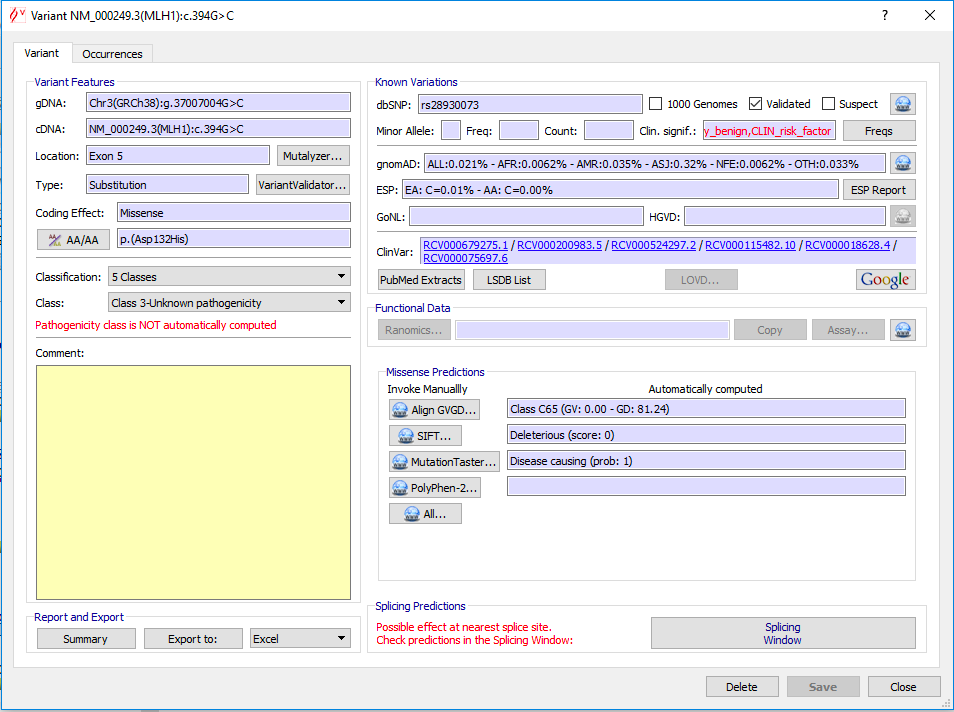 |
The HGVS recommendations for the description of sequence variants implies that for all descriptions the most 3' position possible is arbitrarily assigned to have been changed. Application of this recommendation can make variant entering in Alamut® Visual sometimes disconcerting, since entering a variant may result in a variant located at a different position. The point is that both mutated sequences – entered and resulted – are identical.
For instance:
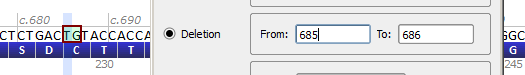
| Variant entered | NM_000546.4(TP53):c.685_686del |
 | |
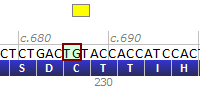
| Variant resulted | NM_000546.4(TP53):c.686_687del |
 | |
| Reference sequence | ...CTCTGACTGTACCACC... |
| Mutated sequence – entered | ...CTCTGAC--TACCACC... |
| Mutated sequence – resulted | ...CTCTGACT--ACCACC... |
Another case:
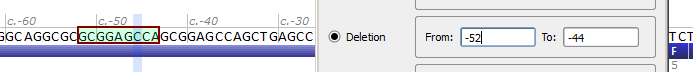
| Variant entered | NM_000352.3(ABCC8):c.-52_-44del |
 | |
| Variant resulted | NM_000352.3(ABCC8):c.-41_-33del |
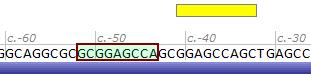 | |
| Reference sequence | ...GCAGGCGCGCGGAGCCAGCGGAGCCAGCTGAGC... |
| Mutated sequence – entered | ...GCAGGCGC---------GCGGAGCCAGCTGAGC... |
| Mutated sequence – resulted | ...GCAGGCGCGCGGAGCCAGC---------TGAGC... |
Variants can be classified using two classification schemes:
You can choose the classification scheme of each variant in the variant annotation window:
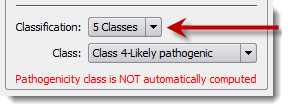
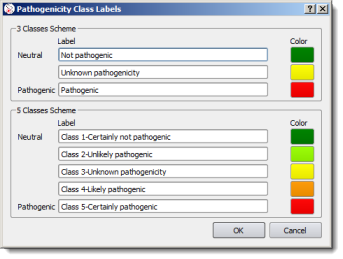
The default classification scheme can be set in the Options dialog box (menu 'Tools' > 'Options' > 'Preferences' tab) and pathogenicity classes and colors can be customized as well:
 |
 |
 |
Beside the pathogenic status of the variant, you can record different occurrences of the same variant. To create an occurrence, click on the 'New Occurrence' button. In the occurrence panel, you can then enter specific information about the case at hand. Fields RNA Analysis, Phenotype and Comment are enabled with a rich text editor.
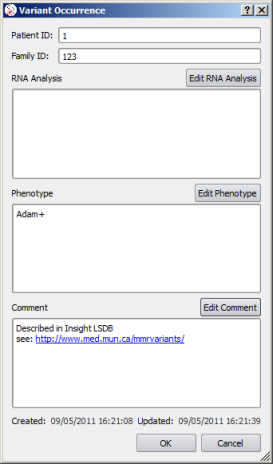 |
Edit Comment |
 |
Once you have created (or modified) an occurrence, the annotation window gets updated. At this point, you should save your changes:
 |
 |
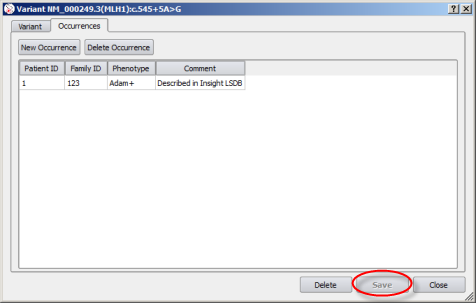 |
Variants are displayed graphically in the main Alamut® Visual window, in the transcript track, above the sequence:
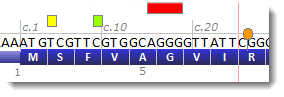
Substitutions, deletions and indels are represented as rectangles, and insertions and duplications as discs at the point of insertion. The color of variant graphic items depends on pathogenicity annotations. By default:
| 3-classes scheme | 5-classes scheme |
|---|---|
| Not pathogenic: green | Class 1- Certainly not pathogenic green |
| Class 2 - Unlikely pathogenic light green | |
| Unknown pathogenicity: yellow | Class 3 - Unknown pathogenicity yellow |
| Class 4 - Likely pathogenic orange | |
| Pathogenic: red | Class 5 - Certainly pathogenic red |
To re-open a variant annotation window, click on its graphical representation.
© 2020 Interactive Biosoftware - Last modified: 30 December 2017